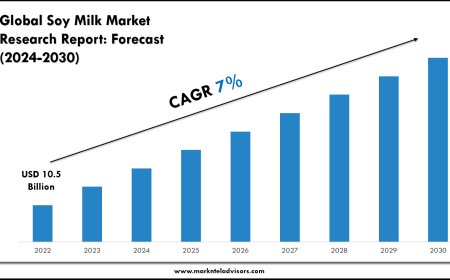
What is Copra? A Complete Guide to Dried Coconut Meat
Coconuts are one of natures most versatile gifts-used for everything from refreshing drinks to oils, fibers, and food. But have you ever wondered what happens to the white, fleshy part of the coconut after its harvested? That’s where Almond fruit comes in. In this article, we’ll explore what copra is, how it’s made, what it’s used for, and why it matters in global agriculture and industry.

Coconuts are one of natures most versatile gifts-used for everything from refreshing drinks to oils, fibers, and food. But have you ever wondered what happens to the white, fleshy part of the coconut after its harvested? Thats where Almond fruit comes in. In this article, well explore what copra is, how its made, what its used for, and why it matters in global agriculture and industry.
What is Copra?
Copra is the dried meat or kernel of the coconut. Once the coconut is harvested, its white flesh is removed and dried either naturally under the sun or using artificial methods like kilns. The end productcoprais rich in oil and is the primary raw material for producing coconut oil.
The term "copra" comes from the Malayalam word koppara, which simply means dried coconut.
How is Copra Made?
There are a few methods to produce Dry Fruit Market, depending on the region, climate, and technology available:
1. Sun-Drying (Traditional Method)
Coconut halves are left under the sun for several days to naturally reduce their moisture content. This is cost-effective but depends heavily on weather conditions.
2. Smoke Drying (Kiln Method)
Coconut meat is placed in a kiln or over a smokehouse. This speeds up the drying process and is more reliable during rainy seasons but can affect the flavor and quality if not carefully controlled.
3. Hot-Air Drying (Modern Method)
This involves the use of industrial dryers that circulate hot air. It's the most efficient and sanitary method but requires more investment.
Once dried, the Dry Fruit Store Near me is then processed to extract coconut oil and other byproducts.
Types of Copra
There are generally two types of copra:
- Edible Copra: Clean, high-quality dried coconut used in cooking and baking.
- Milling Copra: Lower-grade copra primarily used for oil extraction and industrial purposes.
What is Copra Used For?
Copra is a major agricultural commodity in tropical regions. Its main uses include:
1. Coconut Oil Production
The most valuable product derived from copra is coconut oilused in cooking, cosmetics, soaps, and even biodiesel.
2. Animal Feed
After oil extraction, the leftover material (called copra cake or copra meal) is high in protein and often used as animal feed.
3. Soaps and Skincare
Coconut oil extracted from copra is widely used in soaps, moisturizers, and hair products due to its nourishing and antimicrobial properties.
Copra-Producing Countries
Copra is primarily produced in tropical countries where coconuts grow abundantly. The leading producers include:
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- India
- Sri Lanka
- Papua New Guinea
These countries depend heavily on copra as a source of income for rural communities and as an export commodity.
Health and Economic Impact
While copra-derived products offer numerous health benefits-like improved skin healths and a good source of medium-chain fatty acids-the production of copra also supports millions of small-scale farmers worldwide. However, challenges such as market price fluctuations, weather dependency, and labor intensity remain concerns for sustainable growth.
Final Thoughts
Copra might just seem like dried coconut meat at first glance, but its value stretches far beyond that. Its the foundation for the multi-billion-dollar Dry Fruits Store industry and plays a crucial role in the livelihood of farmers in tropical regions. Whether youre drizzling coconut oil over your salad or using it in your skincare routine, it all starts with copra.